Notes on quantization of energy
Notes on quantization of energy
Max planck explained that energy from such bodies is emitted in separate or discrete packets of energy known as energy quanta or photo of amount hv where v is the frequency of radiation and he represents Planck’s constant, then energy by the equation
E = nhf
f = c/λ
c is the speed of light
λ is the wavelength
f is the frequency
Atomic Energy Levels
The arrangement of electrons around their nuclei is in a position known as energy levels or electron orbits of electron shells. Electrons in orbit nearest to the nucleus have the highest energy and are said to be in the ground state or lowest levels.
When an electron jumps from one level, say E4 to a lower one E1 a photon of electromagnetic radiation is emitted with energy equal to the energy of the two levels.
hv = E4 – E1
f = c/λn
En – Eo = hfn = hc/ λn
En = energy in the excited state
Eo = ground state energy
Atomic Spectra, Colour and Light Frequency
When gas atoms are executed by heating or by sending an electrical discharged, they give off light which when analyzed consist of a vast number of spectral lines. The line consists of light of one wavelength or color. This type of spectrum is called a line spectrum or the atomic spectrum of the element.
A line spectrum – Is a number of well-defined lines each having a particular frequency or wavelength or colour.
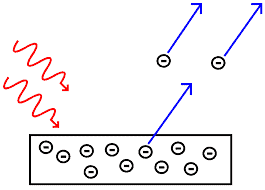
The Photoelectric Effect: This occurs when light falls on metal surfaces, electrons are emitted the emitted electrons called photoelectrons.
Eistein equation
Ek max = hf – wo
wo is the workfunction = hfo
Recommended: How to solve questions on electric field for Cambridge A level and UTME
