Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI operation and uses)
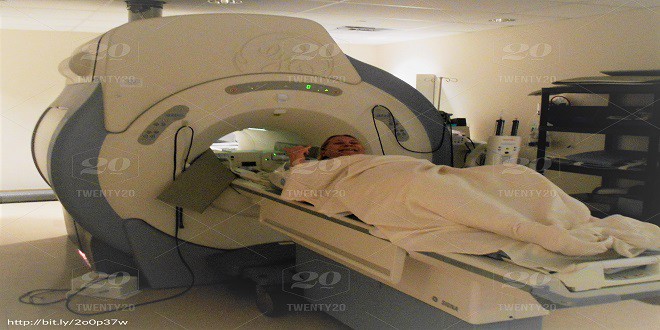
Magnetic resonance imaging, MRI is a diagnostic technique used in medicine. It can provide images of the inside of a patient. It does not rely on exposing patients to ionizing radiation such as x-rays; it relies on the fact that some atomic nuclei behave like tiny magnets in an external magnetic field.
Principle of operation of MRI
Nuclei of hydrogen (and certain other nuclides) have spin/have a magnetic axis. In a strong magnetic field, the nuclei precess about the direction of the field with a frequency known as the Larmor frequency. Radio wave pulse at Larmor frequency causes resonance and nuclei precess in high-energy state. After pulse has ceased, nuclei relax, emitting an RF signal.
How MRI works
MRI scanning involves radio frequency electromagnetic radiation. The patient lies on a bed in strong magnetic field. RF pulse at Larmor frequency transmitted to patient. RF emissions from patient are detected and processed. Hydrogen nuclei within patient have Larmor frequency dependent on magnetic field strength so that location (and concentration) of hydrogen nuclei can be detected. Total image built up by varying the non-uniform field to give specific field strength at different positions within the patient. The receiving coils pick up the relaxation signal and pass it to the computer. Therefore, a picture of the patient’s insides is built up by a computer.
Recommended: Uses and operation of Ultrasound
Component of magnetic resonance imaging
(i) Superconducting magnet
(ii) RF transmission coil
(iii) RF receiver coil
(iv) Gradient coils
(v) Computer
MRI uses
It is use in medical diagnosis (spinal/back problems and fine detail provided of soft and hard tissues)
Advantages of MRI
i) It does not use ionizing radiation which causes a hazard to patients and staff
ii) There are no moving mechanisms, just changing currents and magnetic fields
iii) The patient feels nothing during a scan (although the gradient coils are noisy as they are switched), and there are no after-effects.
iv) MRI gives better soft-tissue contrast than a CT scan, although it does not show bone as clearly
v) Computer images can be generated showing any section through the volume scanned, or as a three-dimensional image
Disadvantage of magnetic resonance imaging
Every metallic objects in the patient, such as surgical pins, can become heated. Loose steel objects must not be felt in the room as these will be attracted to the magnet, and the room must be shielded from external radio fields.
Reference
David Sang et al, Cambridge International AS and A level Physics Coursebook
