Ultrasound: Uses, Operation and how it is generated
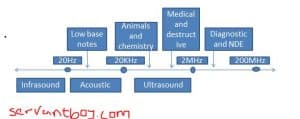
Ultrasound is an oscillating sound pressure wave with a frequency greater than the upper limit of the human hearing range( 20KHz in healthy, young adults). Ultrasound devices operate with frequencies from 20KHz to several gigahertz.
How Ultrasound is generated
i) Like audible sound, ultrasound is produced by a vibrating source. The frequency of the source is the same as the frequency of the waves it produces.
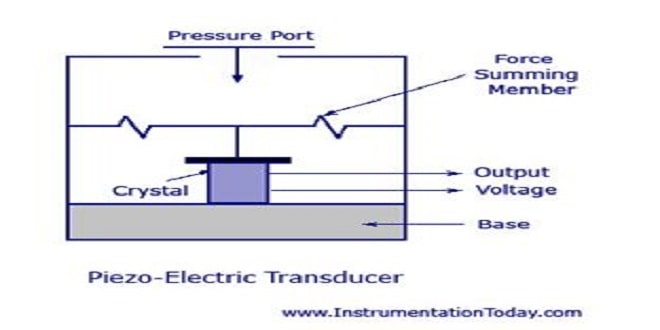
ii) Ultrasound waves may be generated and detected using a piezo-electric transducer.
iii) A transducer converts energy from one form to another.
iv) Electrical energy is converted into ultrasound energy by means of a piezo-electric crystal such as quartz(it is widely used because of its mechanical strength, small dielectric loss, resistance to moisture and the stability of its properties in the face of temperature change).
v) The structure of quartz is made up of a large number of tetrahedral silicate.
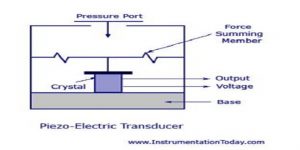
vi) An external electric field is applied to the crystal, the ions in each unit cell are displaced by electrostatic forces, resulting in the mechanical deformation of the whole crystal i.e. expand or contract
vii) An alternating voltage with frequency f causes the crystal to contract and expand at the same frequency f. The alternating voltage applied across the crystal is then acts as the vibrating source of the ultrasound waves.
Uses of Ultrasound
- To detect objects and measure distance
- Sonography(ultrasonic imaging) used both in veterinary and human medicine
- For nondestructive testing of products and structures
- To detect invisible flaws
- For cleaning and for mixing, and to accelerate chemical processes
Principle of Ultrasound scan
There are several different types of ultrasound scan which are used in practice, but their principle are the same(i.e. echo sounding)
- Direct the ultrasound waves into the body
- These waves pass through various tissues and are partially reflected at each other boundary where the wave speed changes
- The reflected waves are then detected and used to construct internal image of the body
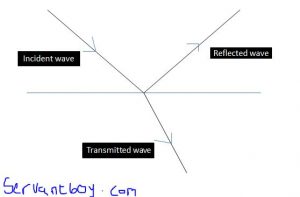
Based on the principle of an ultrasound scan a diagnostic information can be obtained.
A-scan and B-scan are two techniques commonly use for the display of an ultrasound scan.
In an A-scan a pulse of ultrasound is transmitted into the body through the coupling medium. At each boundary between, some of the energy of the pulse is reflected and some transmitted. The transducer detects the reflected pulses. The signal is amplified and displayed on a cathode ray oscilloscope.
Recommended: Short note on electronic sensor
