Quantitative Reasoning Examples and Solutions For Primary 3, 4 & 5

Quantitative Reasoning measures a person’s ability to use mathematical or analytical skills to solve problems. This is to help those in primary schools to understand the logic behind solving any of the given questions in their textbooks. The examples that I solved in this article were obtained from the books recommended for pupils in Nigeria. Here, I will solve some examples for primary 3, 4, and 5 pupils.
Example 1
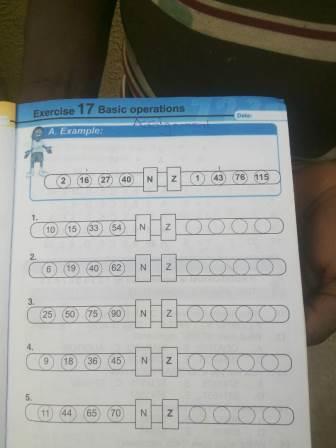
Solution
One good thing about quantitative reasoning is that it helps you think deeply to generate the right answer.
The technique used in the above example follows this pattern;
(2*3) – 5 = 1
(16*3) – 5 = 43
(27*3) – 5 = 76
(40*3) – 5 = 115
Use this format to solve the remaining question
(10*3) – 5 = 25
(15*3) – 5 = 40
(33*3) – 5 = 94
(54*3) – 5 = 157
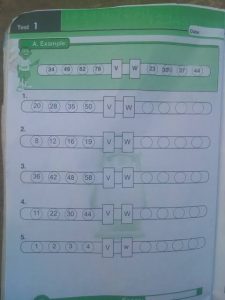
Example 2
Solution
The format to solve this particular question is discussed below;
139 * 3 = 417
258 * 2 = 516
To solve the first question,
113 * 5 = 565
Therefore, 6 will be in the box
Example 3

Solution
(9*4) divided by square root of 9 = 36/3 = 12
(36*5) / square root of 36 = 180/6 = 30
(64*2)/ square root of 64 = 128/8 = 16
Example 4

Solution
The numbers in COLUMN must be the same in the ROW
For ROW 1, the numbers are 1, 2, 3, 0, 1
For COLUMN 1, the numbers are 1, 2, G, 0, T
The G is 3
The T is 1
So, use the same method for the rest.
Example 5

Solution
For the first sample question, take the 2 and 2 in the square boxes to be 22 and multiply the 3 and 6 in the triangle boxes. then subtract i.e. 22-(6*3) = 4 in the circular box
2nd sample: 18-(2*5) = 8
sample 3: 22-(7*3) = 1
Use this approach to solve questions 6-10 of the diagram
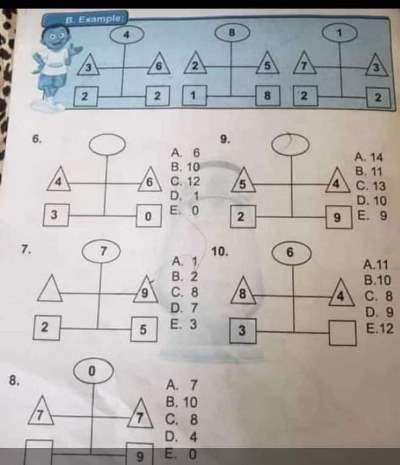
Example 6

Solution
From the samples given, adding the first two columns together will give the third column.
1st example, 4118 + 5420 = 9538
2nd example, 1257 + 3482 = 4739
Also, subtracting the first column from the second column will give you the fourth column.
sample 1, 5420 – 4118 = 1302
sample 2, 3482 – 1257 = 2225
Use this same method to solve questions 1-5 of the diagram
Example 7

Solution
If you look at the first example, add the left-hand side together (7+5+4+3 = 19) and the right-hand side (9+12+15+21 =57). So if you multiply the sum of the left-hand side, which is 19 x 3, you will get the sum of the right-hand side, which is 57
The same for the second example, the left-hand side is 12+5+13+8 = 38, and the right-hand side is 24+36+15+39 = 114. if you multiply the 38 x 3 = 114
In summary, if you add the numbers on the left-hand side and multiply by 3, you will get the sum of the numbers on the right-hand side.
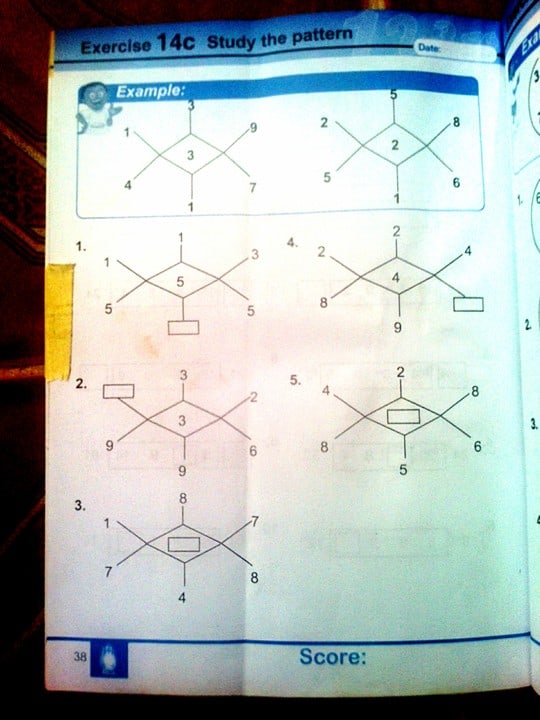
Example 8
solution

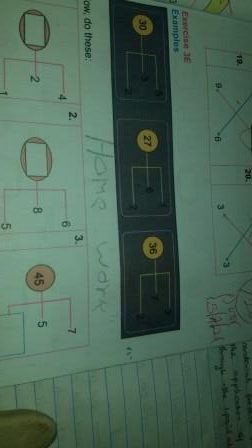
Example 9
Solution
(34/2) + 6 = 23
(49/2) + 6 = 30 1/2
(62/2) + 6 = 37
(76/2) + 6 = 44

For the first sample, the format is
(2+2+1+3)*3=24
(0+4+3+6)*3 =39
(4+1+2+4)*3=33
You add all the numbers at the edge of the diagram and multiply by 3
For the second sample,
2*8=12+4=16
5*9=17+28=45
7*7=25+24=49
Example 11
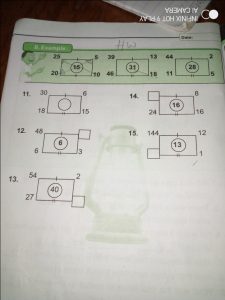
From the example, 25/5 = 5, 20-10 = 10
Then add the two answers 5+10 = 15, which is the number in the middle
For the second one, 39/13 = 3, 46-18 = 28, so 28+3 = 31
For the third one, 44/2 = 23, 11-6 = 5, so 23+5 = 28
Example 12
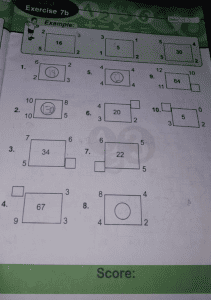
For sample 1, (2^2 + 5^2) -(3^2 + 2^2) = 16
(4 +25) – (9+4) = 16
29-13 = 16
For sample 2, (3^2 + 1^2) – (1^2 + 2^2) = 5
(9 + 1) – (1 + 4) = 5
10 – 5 = 5
For sample 3, (5^2 + 5^2) – (4^2 + 2^2) = 30
(25 + 25) – (16 + 4) = 30
50 – 20 = 30
So, you can use the above approach to solve the remaining questions. If you have any questions on quantitative reasoning, you can link me on Twitter or through my WhatsApp (09059059123).

Please can I get a WhatsApp number so I can be helped fully on the question sir
The number is in the article.
I am a fan.pls make a solution quantitative for book 6
Pls I need help with Test 9 c and d
Test 10 A b and c
In quantitative reasoning book 5