How to solve questions on D.C for UTME and Cambridge A level
Guide on how to solve questions on Direct current(D.C) for UTME and Cambridge A level
It is easy to solve any question on Direct Current (D.C) if you can follow the steps used to solve the questions below. Below are some of the past questions on Direct Current from Cambridge A level hysics and UTME.
Question 1
An electric generator has an e.m.f. of 240V and an internal resistance of 1Ω. If the current supplied by the generator is 20A when the terminal voltage is 220V, find the ratio of the power supplied to the power dissipated.{UTME 2008}
A. 11 : 1 B. 1 : 11 C. 12 : 11 D. 11 : 12
Solution
power supplied = IE
p= 20 * 240 = 4800
power dissipated = IV
p = 20 * 220= 4400 watt
ratio = 4800 / 4400
12 : 11
A is the correct answer
Question 2
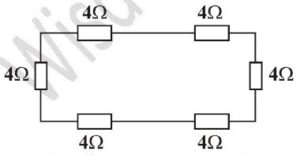
Find the effective resistance in the diagram above.{UTME 2008}
A. 6Ω B. 12Ω C. 16Ω D. 24Ω
solution
the arrangement is series because there is no branching of current
Rt = R1 + R2 + R3 + R4 + R5 + R6
Rt = 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 + 4 + 4
Rt = 24Ω
D is the correct option
Question 3 and 4 are from cambridge may/june 2016 p11
Hurray! It is now free to download the small textbook in pdf that I made for student writing A level physics and UTME. Click to Visit the page to download
Question 3
In the circuit shown, X is a variable resistor whose resistance can be changed from 5.0 Ω to 500 Ω. The e.m.f. of the battery is 12.0 V. It has negligible internal resistance
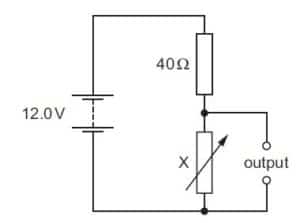
What is the maximum range of values of potential difference across the output?
A 1.3 V to 11.1 V B 1.3 V to 12.0 V C 1.5 V to 11.1 V D 1.5 V to 12.0 V
Solution
Vout = (Rx / Rx + 40)* Vin
since Rx is a variable resistor, the vout will give a varying voltage
when Rx is 5Ω
Vout = (5 / 5 +40)* 12
Vout = 1.3 V
When Rx is 500 Ω
Vout =( 500 / 500 + 40)* 12
Vout = 11.1 V
so Vout will range from 1.3 v to 11.1 v
A is the correct option
Question 4
There is a current from P to R in the resistor network shown.
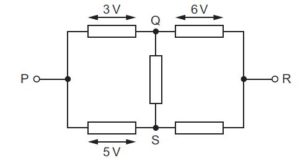
The potential difference (p.d.) between P and Q is 3 V.
The p.d. between Q and R is 6 V.
The p.d. between P and S is 5 V.
Which row in the table is correct?
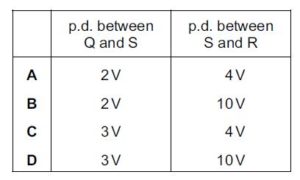
Solution
potential difference between Q and S = p.d. between P and S is 5 V – potential difference (p.d.) between P and Q is 3 V.
potential difference between Q and S = PS – PQ
potential difference between Q and S = 5 – 3 = 2v
also,
potential difference between Q and S= The p.d. between Q and R is 6 V – potential difference between S and R
2 = 6 – SR
SR = 4 v
A is the correct option
Question 5
A battery of electromotive force (e.m.f.) 9.0 V and internal resistance 0.25 Ω is connected in series with two identical resistors X and a resistor Y, as shown in Fig below
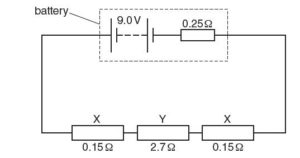
The resistance of each resistor X is 0.15 Ω and the resistance of resistor Y is 2.7 Ω.
(i) Show that the current in the circuit is 2.8 A.
(ii) Calculate the potential difference across the battery.
(iii) Each resistor X connected in the circuit above is made from a wire with a cross-sectional area of 2.5 mm2. The number of free electrons per unit volume in the wire is 8.5 × 10^29 m–3. Calculate the average drift speed of the electrons in X.{cambridge may/ june 2016 p22}
Solution
the resistors are arranged in series
Rt = R1 + R2 + R3
Rt = 0.15 + 2.7 + 0.15
Rt = 3Ω
E = IR + Ir
9 = I (Rt + r)
9 = I ( 3 + 0.25)
9 = 3.25 * I
I = 9 / 3.25
I = 2.8 A
ii.
potential difference across the battery = IRt
p.d = 2.8 * 3
p.d = 8.3 v
iii
I = nevA
n is the number of charge
e is the electronic charge
v is the drift speed
A is the area
I is the current
A = 2.5 mm^2 which in meters will be 2.5 x 10^-6 m^2
v = I / evA
v = 2.77 / (8.5 × 10^29 × 1.6 × 10^–19 × 2.5 × 10^–6)
v = 8.147 x 10^-6 ms-1
Recommended: short note on direct current
