Notes on capacitance of a capacitor for Cambridge A level and UTME
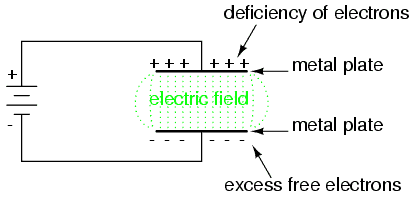
Capacitance of a capacitor is the charge stored on one plate per unit of potential difference between the plates
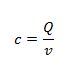
c is the capacitance
Q is the charge
v is the potential difference
Farad is the unit of capacitance
Uses of capacitor
- it stores energy
- smoothing circuit
- separate charges
- blocking D.C
- tuning circuit
- preventing sparks
- timing circuit
- producing electrical oscillations
Explain why the capacitor stores energy but not charge
– capacitor has equal magnitude of +ve and -ve charge
– total charge on capacitor is zero or no resultant charge
– energy stored because there is charge separation
What determines the magnitude of capacitance
- distance between the two plates
- Area of overlap of the two plates
- dielectric material
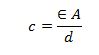
- An isolated metal sphere of radius R has charge +Q on it. The charge may be considered to act as a point charge at the centre of the sphere. Show that the capacitance C of the sphere is given by the expression
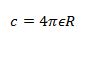
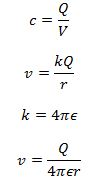
substitute the expression for v in c = Q/v
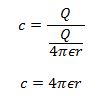
- derive, using the formula C= Q/V , conservation of charge and the addition of p.d.s, formulae for capacitors in series and in parallel
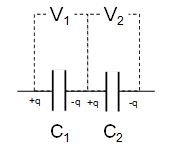
V = V1 + V2
V1 = q / C1 and V2 = q / C2 (q = charge induced on one plate)
q / C = q / C1 + q / C2
1 / C = 1 / C1 + 1 / C2
Parallel arrangement
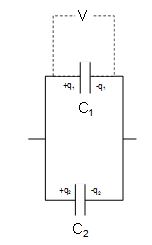
q = q1 + q2
q1 = C1V q2 = C2V
CV = C1V + C2V
C = C1 + C2
Energy stored in a capacitor
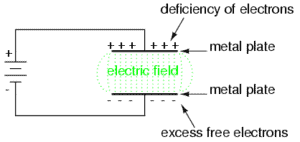
In other to charge a capacitor work must be done to push electrons onto one plate and off the other. The current stops when the p.d across the capacitor is equal to the e.m.f of the supply. We then say that the capacitor is “fully charged”
Uncharge plates has equal amount of +ve and -ve charge. Connecting the capacitor to supply pulls charge +Q from one plate and transfers it to the other, leaving behind charge -Q. The supply does work in separating the charges. Since the two plates now store equal and opposite charges, the total charge on the capacitor is zero. When we talk about “charge stored” by capacitor, we mean the quantity Q, the magnitude of the charge stored on each plate.
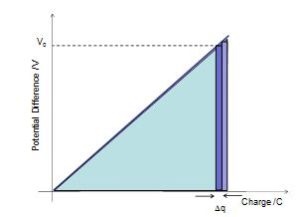
Q = CV
W= Ep = VQ
DEp = V0Dq
W = Ep = ½ QV
W = Ep = ½ CV2
Questions and answers to A level and UTME past questions on capacitance of a capacitor
