Wave Motion And Points On Wave For Cambridge A level And UTME
In this article, I will discuss part of wave (e.g lowest and highest point of waves) and classes of waves. A wave allows energy to be transferred from one point to another without any particle of the medium traveling between the two points.
Classes of Waves
Wave motion can be classified base on:
- Mode of Propagation
The class of waves under this are
Mechanical wave: this requires a material medium for propagation
Electromagnetic wave: This travels in a vacuum
- Mode of vibration
The class of waves under this are:
(i) Longitudinal waves
(ii) Transverse waves
Diagramatic representation of waves
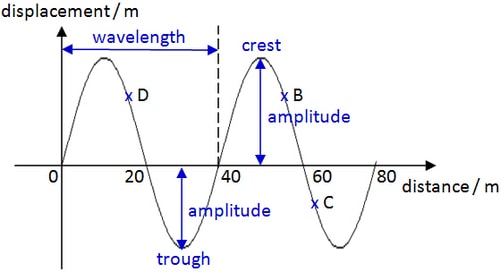
Points On A Wave
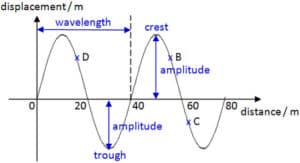
- Rest position – the undisturbed position of particles when they are not vibrating.
- Peak or Crest – the highest point above the rest position.
- Trough – the lowest point below the rest position.
- Amplitude – the maximum displacement of a point of a wave from its rest position.
- Period (T): it is the time taken for a particle to undergo one complete cycle of oscillation.
- Frequency (f): it is the number of oscillations performed by a particle per unit time.
- Wavelength (λ): it is the distance between any two successive particles that are in phase, e.g. it is the distance between 2 consecutive crests or 2 troughs.
- Wave speed (v): The speed at which the waveform travels in the direction of the propagation of the wave.
- Wave front: A line or surface joining points which are at the same state of oscillation, i.e. in phase, e.g. a line joining crest to crest in a wave.
- Displacement : it is the Position of an oscillating particle from its equilibrium position.
- Amplitude: it is the maximum magnitude of the displacement of an oscillating particle from its equilibrium position.
To deduce V = fλ
![]()
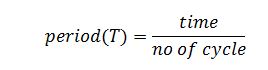
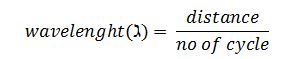
no of cycle = n
time = Tn
distance = λn
substitute all into the velocity = distance/time
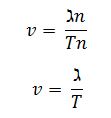
Note
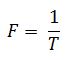
F is the frequency and the S.I base unit is Hertz(Hz)
T is the period and the S.I base unit is second(s)
λ is the wavelength and the S.I base unit is meter(m)
therefore,
V = fλ
Displacement-distance graph and Displacement-time graph
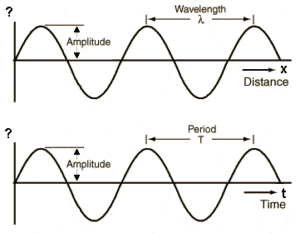
The first graph is a displacement-distance graph. On this graph you can find wavelenght and amplitude
The second graph is a displacement-time graph. On this graph you can find period, frquency and amplitude
The only difference between the two graphs is what you can calculate from it.
Phase difference: this is an amount by which one oscillation leads or lags behiod another. it measures in degree or radian.
Phase difference between waves that are exactly out of phase is π radians or 180 degrees
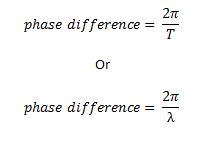
progressive wave: it is a propagation of energy as a results of vibrations of waves which move energy from one place to another.
Intensity: it is defined as power incident per unit area. The intensity of wave generally decreases as it travels along. The two reasons for this are:
- The wave may spread out
- The wave may be absorbed or scattered
As wave spread out, its amplitude decreases
Read: Longitudinal and Transverse waves
The unit of intensity is ![]()
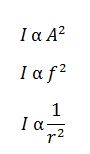
I is the intensity
A is amplitude
f is frequency
r is the distance from the source
Electromagnetic waves travel with the same speed in space
the speed of electromagnetic wave is 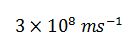
Recommended: Solved questions on wave motion
Related Article: Short note on oscillation
Frequently Asked Questions On Waves
- What is the lowest point on a wave: The lowest point is the trough
- What is the highest point on a wave – Crest
