How to solve questions on Work, Energy and Power
This article provides steps on how to solve questions on Work, Energy and Power. Therefore, the solutions below gives an easy step to how to solve questions on work, Energy, and Power for students writing Cambridge A level and other exams like UTME or Post UTME.
Power: It is the rate of energy expended per unit time. Its unit is Watt
Energy: It is the ability to do work .Its unit is Joule
How to solve questions on Work, Energy and Power
Question 1
A hammer with 10 J of kinetic energy hits a nail and pushes it 5.0 mm into a plank. Both the hammer and nail come to rest after the collision. What is the approximate average force that acts on the nail while it moves through 5.0 mm?{ Cambridge A level may/june 2016 p11}
A 0.050 N B 2.0 N C 50 N D 2000 N
Solution
workdone by a net force = change in kinetic energy of a body
F x s = Ek
F x s = 10
F x 0.005 = 10
F = 10 / 0.005
F = 2000N
D is the correct option
Q2, 3 and 4 are from cambridge A level may/june 2016 p13
Question 2
An object of mass 0.30 kg is thrown vertically upwards from the ground with an initial velocity of 8.0 m s–1. The object reaches a maximum height of 1.9 m. How much work is done against air resistance as the object rises to its maximum height?
A 4.0 J B 5.6 J C 9.6 J D 15 J
Solution
workdone by a net force = change in kinetic energy of a body
workdone = 1/2 m v2
v2 = u2 – 2as
v2 = 64 – 2*9.81*1.9
v2 = 64 – 37.278
v2 = 26.722
workdone = 1/2 * 0.3 * 26.722
workdone = 4.0 J
A is the correct option
Recommended: Short note on work, energy and power
Question 3
A racing car has an output power of 300 kW when travelling at a constant speed of 60 m s–1. What is the total resistive force acting on the car?
A 5 kN B 10 kN C 50 kN D 100 kN
solution
power = force x velocity
300000 = force x 60
force = 300000 / 60
force = 5000 = 5KN
A is the correct option
Question 4
The diagram shows the design of a water wheel which drives a generator to produce electrical power. The flow rate of the water is 200 kg s–1. The generator supplies a current of 32 A at a voltage of 230 V.
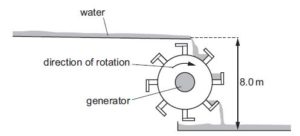
Ignoring any changes in kinetic energy of the water, what is the efficiency of the system?
A 14% B 16% C 22% D 47%
Solution
efficiency = power output / power input
power output = IV
power output = 32*230 = 7360
power input = flow rate * a * h
a is the acceleration due to gravity
power input = 200*8*9.81 = 15696
efficiency = (7360 / 15696)*100%
efficiency = 47%
Q 5 and 6 are from cambridge A level may/june 2016 p12
Question 5
A boy on a bicycle starts from rest and rolls down a hill inclined at 30° to the horizontal. The boy and bicycle have a combined mass of 25 kg. There is a frictional force of 30 N, which is independent of the velocity of the bicycle.
What is the kinetic energy of the boy and the bicycle after rolling 20 m down the slope?
A 1850 J B 2450 J C 3050 J D 3640 J
Solution
mgsinθ – fr = ma
25 * 9.81*sin30 – 30 = ma
122.625 – 30 = ma
92.625 = ma
ma is the net force
the kinetic energy = net force X distance
kinetic energy = 92.625 * 20 = 1852 J = 1850J
A is the correct answer
Question 6
An escalator in an underground station has 250 people standing on it and is moving with a velocity of 4.3 m s–1. The average mass of a person is 78 kg and the angle of the escalator to the horizontal is 40°.
What is the minimum power required to lift these people?
A 54 kW B 64 kW C 530 kW D 630 kW
Solution
the vertical force = mgsinθ = 250*78*9.81*sin40 = 122962 N
minimum power = vertical force x velocity = 122962 x 4.3 = 530 Kw
C is the correct option
Question 7
A man has a mass of 80 kg. He ties himself to one end of a rope which passes over a single fixed pulley. He pulls on the other end of the rope to lift himself up at an average speed of 50 cm s–1.
What is the average useful power at which he is working? (Cambridge A level May/June 2017 p13 q17)
A 40 W B 0.39 kW C 4.0 kW D 39 kW
Solution
Power is the rate of energy expended per unit time i.e power = energy/time = force x velocity
force = mass x acceleration due to gravity. note g in CIE is always 9.81ms-2
f = 80 x 9.81 = 784.8N
velocity in ms-1 = 50/100 = 0.5ms-1
power = 784.8 x 0.5 = 392.4 watt = 0.39KW (B is the correct answer)
Question 8
Calculate the apparent weight loss of a man weighing 70kg in an elevator moving downwards with an acceleration of 1.5ms-2.{2013 UTME Physics – Type U}
A. 105N B. 686N C. 595N D. 581N
solution
when an elevator is moving down
net force = ma
net force = 70*1.5
net force = 105 N
the weight loss = net force
the weight loss = 105 N
A is the correct option
Click here to download for free Preparatory guide Physics for Cambridge A level, Post UTME, and UTME
