5 Types Of Thermometer Physics And Uses
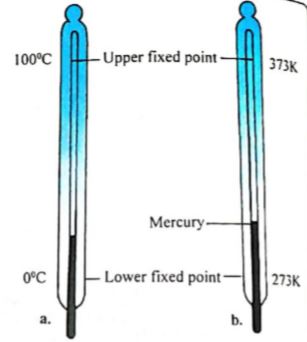
In this article, I will discuss types of thermometers and their uses. Thermometers use any physical property of a substance that varies in a known way with temperature and is easily measurable as a means of gauging temperature. The substance of whose physical property is so used is known as a thermometric substance.
Our sense of touch can give us a general impression of the degree of hotness or coldness of a body. This is however not a reliable method of estimating or measuring a temperature, because the response of the human sense of touch to a temperature change tends to be influenced by its previous experience. Thus warm water will feel cool if a hand initially dipped in hot water is transferred to it. Hence to gauge accurately the exact degree of hotness, an instrument called the thermometer is used. Thermometers are much more reliable instruments for measuring temperatures.
Types
| Type of thermometer | Thermometric substance | Physical property |
| Liquid-in-glass-thermometer | Mercury or Alcohol | Change in volume of liquid with temperature |
| Gas thermometer | Gas | Change of gas pressure at constant volume with temperature |
| Resistance thermometer | Resistance wire | Change in the electrical resistance of wire with temperature |
| thermocouple | Two dissimilar metals (e.g. copper and constantan) | Change in electric potential difference (or current) between two metal junctions at different temperatures |
| Bimetallic thermometer | Two dissimilar metals (e.g. iron and copper) | The differential expansion of the two metals of the bimetallic strip |
Liquid -in-Glass Thermometer
The most common liquids used in thermometers are mercury and alcohol. The thermometer measures temperature by measuring the change in volume of a fixed mass of liquid due to a change in temperature.

For high sensitivity, liquid-in-glass thermometer should have
- A bulb is made of thin glass; this enables the liquid in the bulb to assume the temperature of its surrounding quickly
- A narrow capillary tube with a uniform bore. This makes it possible for small temperature changes to cause large changes in the length of the mercury column.
- A liquid with a high expansivity
To be used as a thermometric liquid, such as a liquid should
- Expand or contract uniformly with temperature
- Have a high boiling point and a low melting point
- Be easily seen in a glass
Water has none of the above properties. It has a small range of expansion; it freezes at 0 degrees and boils at 100 degrees. It does not expand uniformly (it also contracts from 0 degrees to 4 degrees). It wets glass and is colourless, making the meniscus in glass difficult to read. The above reasons make water unsuitable as a thermometric liquid.
Mercury-in-glass thermometers are more commonly used in school laboratories and hospitals than Alcohol-in-glass. Mercury-in-glass thermometer is cheap and simple, but it is not reliable enough for accurate work.
Clinical Thermometer
This is a form of mercury-in-glass thermometer used in the hospital for measuring the temperature of the human body. The temperature of a normal healthy person is about 37 degrees Celsius but it may rise to about 41 degrees in case of high fever. The temperature range of the clinical thermometer is therefore between 35 degrees to 43 degrees Celsius.
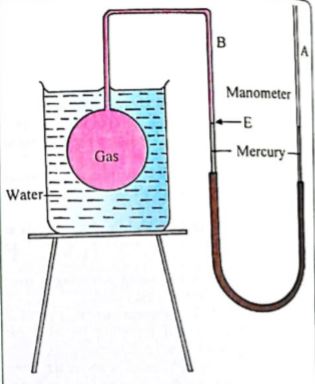
The Gas Thermometers
Gas thermometers are therefore used for accurate temperature measurements. The principle of the gas thermometer is based on the fact that at constant volume, the pressure of a gas increases linearly with an increase in temperature. A constant volume gas thermometer consists of a large bulb which contains a gas (e.g hydrogen or helium). The bulb is connected to a narrow glass tube attached to a mercury manometer.
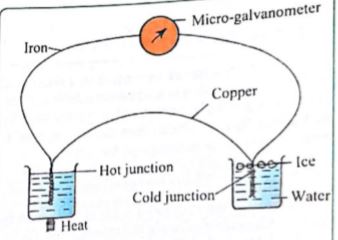
Thermoelectric Thermometer
These thermometers are used for measuring very high temperatures. They work on the principle of the thermocouple. When two different metals (e.g copper and constantan) are joined at the ends and one end (the hot junction) is heated, while the other end (the cold junction) is kept constant in melting the ice, an electric current flows along the metals. This is the thermoelectric effect and setup is called a thermocouple.
Read: Difference between boiling and evaporation
Resistance Thermometer
This is one of the types of thermometer and it uses the fact that the electrical resistance of a metallic conductor changes proportionally with its temperature. The higher the temperature the greater is the resistance. It consists of a long thin platinum wire wound round a small spool made of mica or silica. Resistance thermometers are useful in the accurate measurement of very low or very high temperatures.
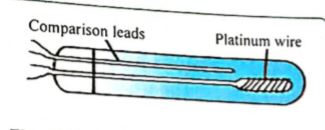
The difference between these two thermometers are
- resistance thermometer is larger than a thermocouple
- has greater thermal capacity therefore slower acting while a thermocouple is smaller,
- has smaller capacity, therefore quicker acting, and can measure temperature at a point.
