Physic Tutorials
Simplifying physics for better understanding for students to excel in ‘A level’ and UTME
-
How to Solve Some JAMB UTME Physics Past Questions
For all candidates writing JAMB physics, this page provides answers to some UTME physics past questions. Question 1 Which of…
Read More » -
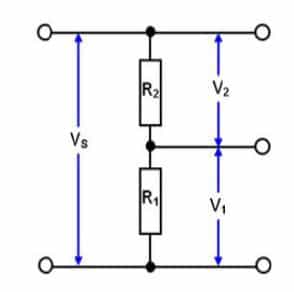
How to Calculate and Solve Potential Divider Problems
A potential divider circuit is arranged in such a way to get an output voltage from a battery of particular…
Read More » -
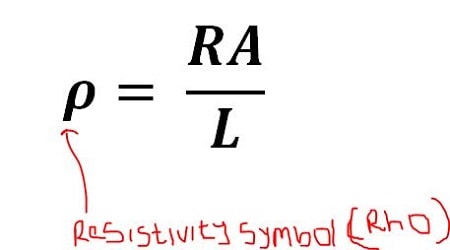
How To Calculate And Solve Questions On Resistivity
In this article, I will define; and give the value of the resistivity of some materials, and how to solve…
Read More » -
Expected Topics And Strategies To Questions In JAMB Physics
From my experience as a tutor and lecturer of physics, I know that there are some repeated topics in physics…
Read More » -
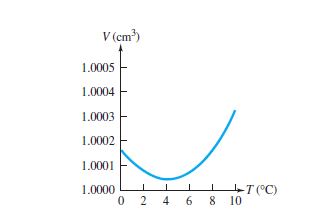
Anomalous Behaviour of Water Explained With Questions
Water behaves anomalously when compared with other liquids at certain temperatures. Most liquid expand when heated and contract when cooled.…
Read More » -
Senior Secondary (SS1) Physics Questions
These SS1 Physics questions below are followed based on the SS1 Physics scheme of work in Nigeria. And if you…
Read More » -

Electric Field Examples And Answers
Electric field is a region of space where a charge experience a force. In this article, I will be providing…
Read More » -
How Does a Capacitor Store Energy
Many of the most important applications of capacitors depend on their ability to store energy and not accumulate and store…
Read More » -
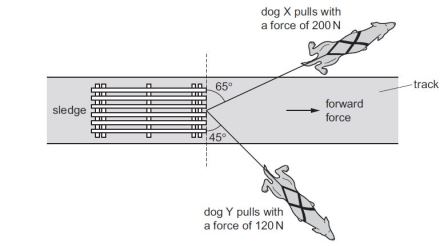
Solutions to CIE Physics May/June And Oct/Nov P1 Questions
Below are few of the soluions to CIE physics 2015, 2016 and 2018 may/june Paper 1 questions. Question 1 What…
Read More » -
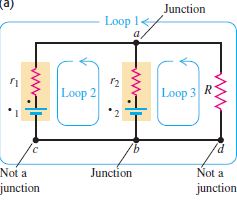
Kirchhoff’s Laws And Their Application
Kirchhoff extended Ohm’s law to networks, and gave two laws, which enable current in any part of the network to…
Read More »
